- Hello Class!
- Today in class we discussed Thanksgiving, a 3 pt. curve on the test, and DNA Notes
- HW- Read chapter 10 if you have not done so, study for the test on Monday 12/5
- Tomorrow- Bring colored pencils to help with notes
DNA NOTES






Discovery of DNA (Important people):
A. Griffith
A. Griffith
- The experiment (1928) - Mixed dead harmful bacteria with living non-harmful bacteria and injected the bacteria into mice. The mice died and when blood samples were taken it showed the bacteria was now living and harmful.
- Proved- The transforming factor in cells that let 1st DNA be inherited to 2nd DNA

B. Hershey and Chase
- The experiment- Did a side by side experiment and Took blended radioactive protein and bacterium, and radioactive DNA and bacterium. Then they centrifuged the mixture and tested for radioactivity. The protein mixture did not have radioactivity but the DNA mixture was radioactive.

- Proved- DNA of the hosts cells reproduced new viruses.
C. Franklin ( & Wilkins) -
- Took X-ray crystakkigraphy of DNA
- Proved- DNA has a helical nature ( twists)

This photo, nicknamed Photo 51 showed the helical structure of DNA
D. Watson and Crick (1953)
- Made the first model of DNA
- Discovered base pairing
- Discovered the double helix
Double Helix-

- 1962- Watson, Crick, and Wilkins won nobel prize, not Franklin, because she had passed away
II DNA Structure:
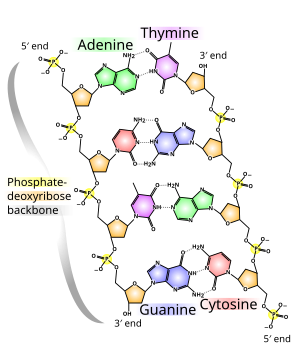
- Double helix-a pair of parrelel helices intertwined about a common axis
- Ex. Structure of a DNA molecule :)
- NO central balance

- Nucleic acid = polynucleotides
- 4 nucleotides
- A=Adenine, T=Thymine, G=Gaunine, C=Cytoine
- A pairs with T, C paires with G ONLY!!!
- T and C are prymindines ( single ring )
- A and G are purines ( double ring )
- They form hydrogen bonds with eachother ( weak )

- N bases protrude from sugar
- Base can not form a bond with phosphate
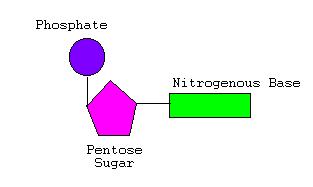
- Sugar and phosphate are the backbones (sides) of the DNA
- Sugar is deoxyribose ( without oxygen )
- A nucleotide is a nitrogen base, a sugar, and a phosphate

- Nucleotides are joined together by covalent (strong) bonds between sugar and phosphate
III. DNA Replication
- Occurs in nucleous
- Parent DNA untwists
- N bases attach to complementary base
- Forms 2 daughter DNA molecules
- The daughter molecules rewind as they form

- Occurs at a rate of 50 nucleotides a second
- Only 1/1 bil are incorrectly paired
- DNA can be harmed by: UV rays, toxic chemicals, and viruses
- Replication begins at origins and goes in both directions, creating replication bubbles
- This is to speed up the process

Beadle and Tatum
- 1 gene produces 1 specific enzyme/polypeptide
- Sections of DNA codes for certain amino acids
- 20 different animoacids to code for
That's about it guys!
NEXT SCRIBE- REGINA!
Hey Minji, i think you did a good job here. But the one thing i recommend is that maybe you should have gone more in depthe when talking about Watson and Cricks experiment, or maybe explained the picture you put in. But great job!
ReplyDeleteMinji! Great post. The pictures were so helpful for me. You used plenty so it really helped me grasp what we covered in class.Great Job!
ReplyDeleteMinji, awesome job on the blog post! You had very nice a colorful pictures and I do agree you could've added more information about Watson and Crick. Great Job! See you in class!
ReplyDelete~Nazia