- Naked Egg Demo; Day 2
- Notes- Mitosis and Cancer
- Lab- Mitosis p. 53-56
Homework:
- Work on Labs
- Internet Activities p. 5 (for review)
- Study for Test on Tuesday 10/11
We reobserved Day 2 of the egg demo due to difficulties with the first egg. The egg's shell has dissapeared in majority of places, and the hard surface of the egg is now replaced with a soft surface. It looks as if there are bubbles stuck all over the cell.
The picture shows the results of an egg standing in vinegar for 24 hours.
Why do cells divide?
- replacement of lost or damaged cells
- reproduction of organisms
- growth
- pass genes from cell to cell
- single celled to multicellular
Sexual Reproduction
- requires fertilization
- only in reproductive organs
- sperm and egg contain half of chromosomes
- meiosis
Asexual Reproduction:
- fertilization not needed
- parent & offspring have identical genes
- binary fision
- mitosis
Chromosomes:
- contain all genes of eukaryotic cell
- chromatin- diffuse mass of long thin fibers, combination of DNA, and protein (cannot be seen during interphase)
- before division, chromotin (make up chromosomes) coils up to form distinct chromosomes
- humans have 46 chromosomes
- number of chromosomes and number of genes dependent on species but not on complexity
Chromsome Replication
- genetic material bedoubled before ell division to ensure daughter chromsomes are identical to parent
- sister chromotoids- identical copies of eachother; attached at centriole
- daughter cells- cells thatr esult from cell division
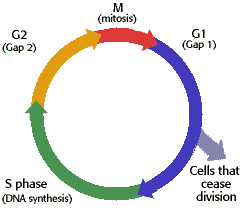
Cell Cycle
To the Right: Diagram of Cell Cycle
Interphase
- 90% of cell cycle
- cell metabolizes and performs functions inside organism
- cell doubles everything in cytoplasm
- chromosomes in the from of chromotin
Steps In Interphase
- G= gap
- G1- organelles double, cells grow in size
- S= synthesis (DNA)
- most important event is chromosome replication (occurs in nucleus)
- G2- final preparation before division
Early Prophase
- Chromosomes coil and condense to become visible
- nucleoli dissapears
- sister chromotids poresent and held together by centriome
- spindle begins to form
Late Prophase
- nuclear envelope breaks down
- spindle attaches to centromer and moves chromosomes towards center
- Spindle is completely formed
- centriomers on chromosomes are line dup on the imaginary equator between pole

- spindle attached to sister chromotoid
Anaphase
- sister chromotoids seperated and now daughter cells a chromosome
- motor proteins move to sides of cell
- spindle microtubules that are attached to chromosomes lengthen to elongate the cell and force the poles further apart in preparation for daughter cells
Telophase
- begins when chromosomes reach poles
- reverse of prophase: nuclear envelope reappear, chromosomes uncoil, nucleoli reappears, and spindle dissapears
- Mitosis is now finished
- cytokinesis has already begun

Diagram of Mitosis
Cell Cycle Control
- cells that are not detected by cell cyc;e control system tend to divide out of control
- can result to benign tumor
- can cause problems depending on where they are
- always remain original size
- displaces normal tissue
What is Cancer?
- cancer cells have faulty cell cycle, divide out of copntrol and demonstrate bizarrre behavior
- malignant tumor- lump that results from the division of a cancer cell
- can spread into nearby tissue or other parts of the body
- displaces normal tissue as grows
- can spread into circulatory system
- metastatis- spread of cancer cells
Mitosis Lab
Materials
- microscope
- prepared slides of onion roots
- dinal section
Procedure
- locate with a microscope the region of rapidly dividing cells on the prepared slide of onion root
- locate cells that appear to be in the various stages of mitosis
- identify and label the following stages :
-interphase
-prophase
-mataphase
-anaphase
-telophase
-daughter cells
Sincerely,
Brianna
NEXT SCRIBE: OLIVIA

Good Job on the Scribe Post!
ReplyDeleteYou laid our your information in an easy to read format. The colors helped highlight sections as well. You may want to add pictures to further explain your information but you did a great job!
Thanks,
Siddharth Rajan